Toward Efficient Agents: A Survey of Memory, Tool learning, and Planning
Abstract
Recent years have witnessed increasing interest in extending large language models into agentic systems. While the effectiveness of agents has continued to improve, efficiency, which is crucial for real-world deployment, has often been overlooked. This paper therefore investigates efficiency from three core components of agents: memory, tool learning, and planning, considering costs such as latency, tokens, steps, etc. Aimed to conducting comprehensive research addressing the efficiency of the agentic system itself, we review a broad range of recent approaches that differ in implementation yet frequently converge on shared high-level principles including but not limited to bounded context via compression and retrieval, reduced action cost via budgeted tool use and caching, and controlled search via hierarchical planning and pruning for improving efficiency, which we discuss in detail. Accordingly, we characterize efficiency in two complementary ways: comparing effectiveness under a fixed cost budget, and comparing cost at a comparable level of effectiveness. This trade-off can also be viewed through the Pareto frontier between effectiveness and cost. From this perspective, we also examine efficiency oriented benchmarks by summarizing evaluation protocols for these components and consolidating commonly reported efficiency metrics from both benchmark and methodological studies. Moreover, we discuss the key challenges and future directions, with the goal of providing promising insights.
Paper List Navigation
📑 Table of Memory Contents
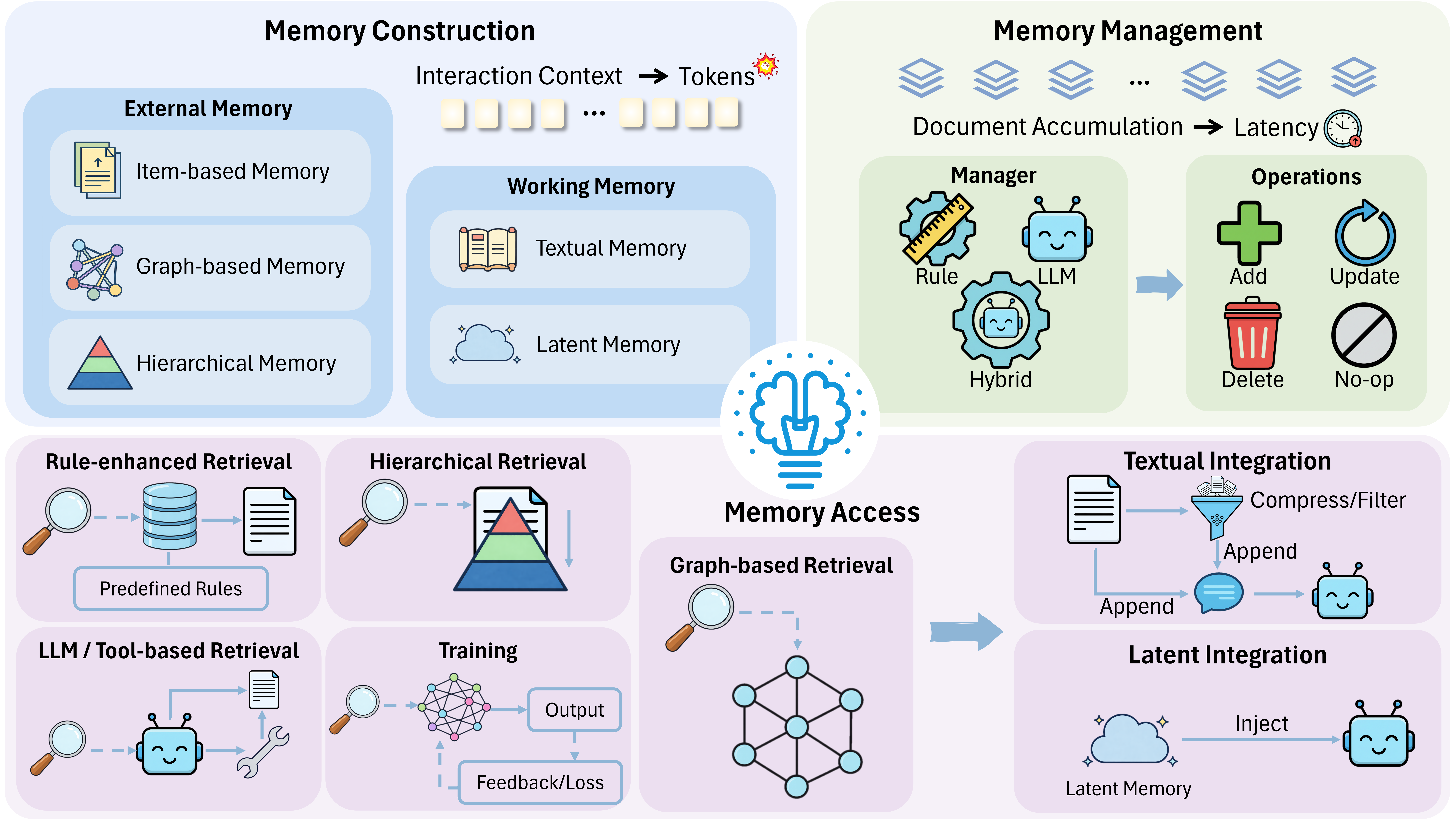
In the paper, we organize memory into construction, management, and access. Since many papers overlap across these stages, this part is primarily organized around memory construction to avoid redundancy.
🔄 Working Memory
📝 Textual Memory
- (2025-10) AgentFold: Long-Horizon Web Agents with Proactive Context Management
- (2025-07) MemAgent: Reshaping Long-Context LLM with Multi-Conv RL-based Memory Agent
- (2025-06) MEM1: Learning to Synergize Memory and Reasoning for Efficient Long-Horizon Agents NeurIPS WS 2025 COLM WS 2025
- (2025-04) Dynamic Cheatsheet: Test-Time Learning with Adaptive Memory
- (2024-02) Compress to Impress: Unleashing the Potential of Compressive Memory in Real-World Long-Term Conversations COLING 2025
🧩 Latent Memory
- (2026-01) FlashMem: Distilling Intrinsic Latent Memory via Computation Reuse
- (2025-09) MemGen: Weaving Generative Latent Memory for Self-Evolving Agents
- (2025-02) M+: Extending MemoryLLM with Scalable Long-Term Memory ICML 2025
- (2025-01) Titans: Learning to Memorize at Test Time
- (2024-09) MemoRAG: Boosting Long Context Processing with Global Memory-Enhanced Retrieval Augmentation TheWebConf 2025
- (2024-07) Memory³: Language Modeling with Explicit Memory
- (2024-02) MEMORYLLM: Towards Self-Updatable Large Language Models ICML 2024
- (2024-01) Long Context Compression with Activation Beacon ICLR 2025
💾 External Memory
📦 Item-based Memory
- (2026-01) MemRL: Self-Evolving Agents via Runtime Reinforcement Learning on Episodic Memory
- (2025-10) Agentic Context Engineering: Evolving Contexts for Self-Improving Language Models
- (2025-09) ReasoningBank: Scaling Agent Self-Evolving with Reasoning Memory
- (2025-08) Memory-R1: Enhancing Large Language Model Agents to Manage and Utilize Memories via Reinforcement Learning
- (2025-08) Memento: Fine-tuning LLM Agents without Fine-tuning LLMs
- (2025-07) Agent KB: Leveraging Cross-Domain Experience for Agentic Problem Solving ICML 2025 Workshop
- (2025-06) Cost-Efficient Serving of LLM Agents via Test-Time Plan Caching (Agentic Plan Caching: Test-Time Memory for Fast and Cost-Efficient LLM Agents) NeurIPS 2025
- (2025-04) Mem0: Building Production-Ready AI Agents with Scalable Long-Term Memory
- (2025-03) MemInsight: Autonomous Memory Augmentation for LLM Agents EMNLP 2025
- (2025-03) In Prospect and Retrospect: Reflective Memory Management for Long-term Personalized Dialogue Agents ACL 2025
- (2025-02) A-MEM: Agentic Memory for LLM Agents NeurIPS 2025
- (2025-02) On Memory Construction and Retrieval for Personalized Conversational Agents ICLR 2025
- (2024-06) Hello Again! LLM-powered Personalized Agent for Long-term Dialogue NAACL 2025
- (2024-04) "My agent understands me better": Integrating Dynamic Human-like Memory Recall and Consolidation in LLM-Based Agents CHI EA 2024
- (2023-10) RECOMP: Improving Retrieval-Augmented LMs with Compression and Selective Augmentation ICLR 2024
- (2023-08) ExpeL: LLM Agents Are Experiential Learners AAAI 2024
- (2023-08) MemoChat: Tuning LLMs to Use Memos for Consistent Long-Range Open-Domain Conversation
- (2023-05) MemoryBank: Enhancing Large Language Models with Long-Term Memory AAAI 2024
🕸️ Graph-based Memory
- (2026-01) MAGMA: A Multi-Graph based Agentic Memory Architecture for AI Agents
- (2025-10) D-SMART: Enhancing LLM Dialogue Consistency via Dynamic Structured Memory And Reasoning Tree
- (2025-04) Mem0: Building Production-Ready AI Agents with Scalable Long-Term Memory
- (2025-01) Zep: A Temporal Knowledge Graph Architecture for Agent Memory
- (2024-07) AriGraph: Learning Knowledge Graph World Models with Episodic Memory for LLM Agents IJCAI 2025
- (2024-06) GraphReader: Building Graph-based Agent to Enhance Long-Context Abilities of Large Language Models EMNLP 2024 Findings
- (2024-02) KG-Agent: An Efficient Autonomous Agent Framework for Complex Reasoning over Knowledge Graph ACL 2025
🪜 Hierarchical Memory
- (2025-10) Beyond a Million Tokens: Benchmarking and Enhancing Long-Term Memory in LLMs ICLR 2026
- (2025-10) LightMem: Lightweight and Efficient Memory-Augmented Generation
- (2025-07) Hierarchical Memory for High-Efficiency Long-Term Reasoning in LLM Agents
- (2025-07) MemOS: A Memory OS for AI System
- (2025-06) Memory OS of AI Agent EMNLP 2025
- (2024-08) HiAgent: Hierarchical Working Memory Management for Solving Long-Horizon Agent Tasks with Large Language Model ACL 2025
- (2024-02) A Human-Inspired Reading Agent with Gist Memory of Very Long Contexts ICML 2024
- (2023-10) MemGPT: Towards LLMs as Operating Systems
👥 Multi-Agent Memory
🏠 Local Memory
- (2025-08) Intrinsic Memory Agents: Heterogeneous Multi-Agent LLM Systems through Structured Contextual Memory
- (2025-04) AgentNet: Decentralized Evolutionary Coordination for LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems NeurIPS 2025
- (2025-02) LLM-Powered Decentralized Generative Agents with Adaptive Hierarchical Knowledge Graph for Cooperative Planning
🔀 Mixed Memory
- (2025-10) LEGOMem: Modular Procedural Memory for Multi-agent LLM Systems for Workflow Automation AAMAS 2026 Extended Abstract
- (2025-05) Collaborative Memory: Multi-User Memory Sharing in LLM Agents with Dynamic Access Control
- (2025-01) SRMT: Shared Memory for Multi-agent Lifelong Pathfinding
📑 Table of Tool Learning Contents
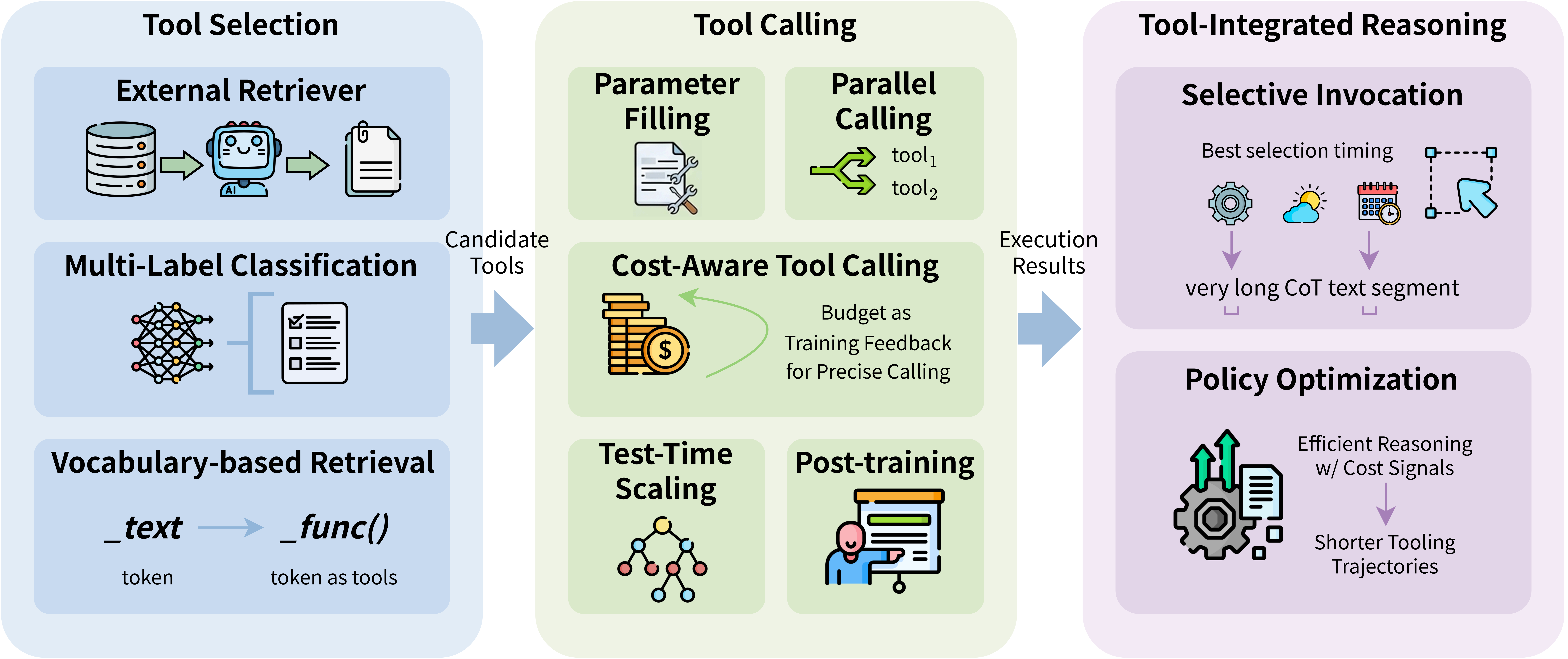
Tool Learning framework encompasses tool selection, tool calling, and tool-integrated reasoning for enhanced agent capabilities.
🔧 Tool Selection
🔍 External Retriever
- (2025-10) ToolScope: Enhancing LLM Agent Tool Use through Tool Merging and Context-Aware Filtering
- (2024-10) Toolshed: Scale Tool-Equipped Agents with Advanced RAG-Tool Fusion and Tool Knowledge Bases ICAART 2025
- (2024-10) From Exploration to Mastery: Enabling LLMs to Master Tools via Self-Driven Interactions ICLR 2025 oral
- (2024-02) AnyTool: Self-Reflective, Hierarchical Agents for Large-Scale API Calls ICML 2024
- (2023-12) ProTIP: Progressive Tool Retrieval Improves Planning EACL 2024 Workshop
🏷️ Multi-Label Classification (MLC)
- (2024-09) Efficient and Scalable Estimation of Tool Representations in Vector Space
- (2024-09) TinyAgent: Function Calling at the Edge EMNLP 2024 Demo
📚 Vocabulary-based Retrieval
- (2025-03) Chain-of-Tools: Utilizing Massive Unseen Tools in the CoT Reasoning of Frozen Language Models
- (2024-10) Toolken+: Improving LLM Tool Usage with Reranking and a Reject Option EMNLP 2024 Findings
- (2024-10) ToolGen: Unified Tool Retrieval and Calling via Generation ICLR 2025
- (2024-07) Concise and Precise Context Compression for Tool-Using Language Models ACL 2024 Findings
- (2023-05) ToolkenGPT: Augmenting Frozen Language Models with Massive Tools via Tool Embeddings NeurIPS 2023 oral
▶️ Tool Calling
📝 In-Place Parameter Filling
- (2024-01) Efficient Tool Use with Chain-of-Abstraction Reasoning COLING 2025
- (2023-02) Toolformer: Language Models Can Teach Themselves to Use Tools NeurIPS 2023 oral
⚡ Parallel Tool Calling
- (2026-02) W&D: Scaling Parallel Tool Calling for Efficient Deep Research Agents
- (2024-11) CATP-LLM: Empowering Large Language Models for Cost-Aware Tool Planning ICCV 2025
- (2024-05) An LLM-Tool Compiler for Fused Parallel Function Calling
- (2023-12) An LLM Compiler for Parallel Function Calling ICML 2024
💰 Cost-Aware Tool Calling
- (2025-07) A Joint Optimization Framework for Enhancing Efficiency of Tool Utilization in LLM Agents ACL 2025 Findings
- (2025-05) Distilling LLM Agent into Small Models with Retrieval and Code Tools
- (2025-03) Alignment for Efficient Tool Calling of Large Language Models EMNLP 2025
- (2025-02) ToolCoder: A Systematic Code-Empowered Tool Learning Framework for Large Language Models ACL 2025
- (2024-02) Budget-Constrained Tool Learning with Planning ACL 2024 Findings
- (2024-01) TroVE: Inducing Verifiable and Efficient Toolboxes for Solving Programmatic Tasks ICML 2024
⚙️ Efficient Test-Time Scaling
🎯 Efficient Tool Calling with Post-training
🛠️ Tool-Integrated Reasoning (TIR)
✅ Selective Invocation
- (2025-09) TableMind: An Autonomous Programmatic Agent for Tool-Augmented Table Reasoning WSDM 2026
- (2025-05) Tool-Star: Empowering LLM-Brained Multi-Tool Reasoner via Reinforcement Learning
- (2025-02) SMART: Self-Aware Agent for Tool Overuse Mitigation ACL 2025 Findings
- (2024-03) Agent-FLAN: Designing Data and Methods of Effective Agent Tuning for Large Language Models ACL 2024 Findings
🎓 Cost-Aware Policy Optimization
- (2026-01) ET-Agent: Incentivizing Effective Tool-Integrated Reasoning Agent via Behavior Calibration
- (2025-10) PORTool: Tool-Use LLM Training with Rewarded Tree
- (2025-10) A$^2$FM: An Adaptive Agent Foundation Model for Tool-Aware Hybrid Reasoning
- (2025-09) Toward Effective Tool-Integrated Reasoning via Self-Evolved Preference Learning
- (2025-09) TableMind: An Autonomous Programmatic Agent for Tool-Augmented Table Reasoning WSDM 2026
- (2025-07) Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization
- (2025-07) AutoTIR: Autonomous Tools Integrated Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
- (2025-05) Reinforced Internal-External Knowledge Synergistic Reasoning for Efficient Adaptive Search Agent
- (2025-05) Agentic Reasoning and Tool Integration for LLMs via Reinforcement Learning
- (2025-04) ToolRL: Reward is All Tool Learning Needs NeurIPS 2025
- (2025-04) ReTool: Reinforcement Learning for Strategic Tool Use in LLMs
- (2025-04) Synthetic Data Generation & Multi-Step RL for Reasoning & Tool Use COLM 2025
- (2025-04) Acting Less is Reasoning More! Teaching Model to Act Efficiently
📑 Table of Planning Contents
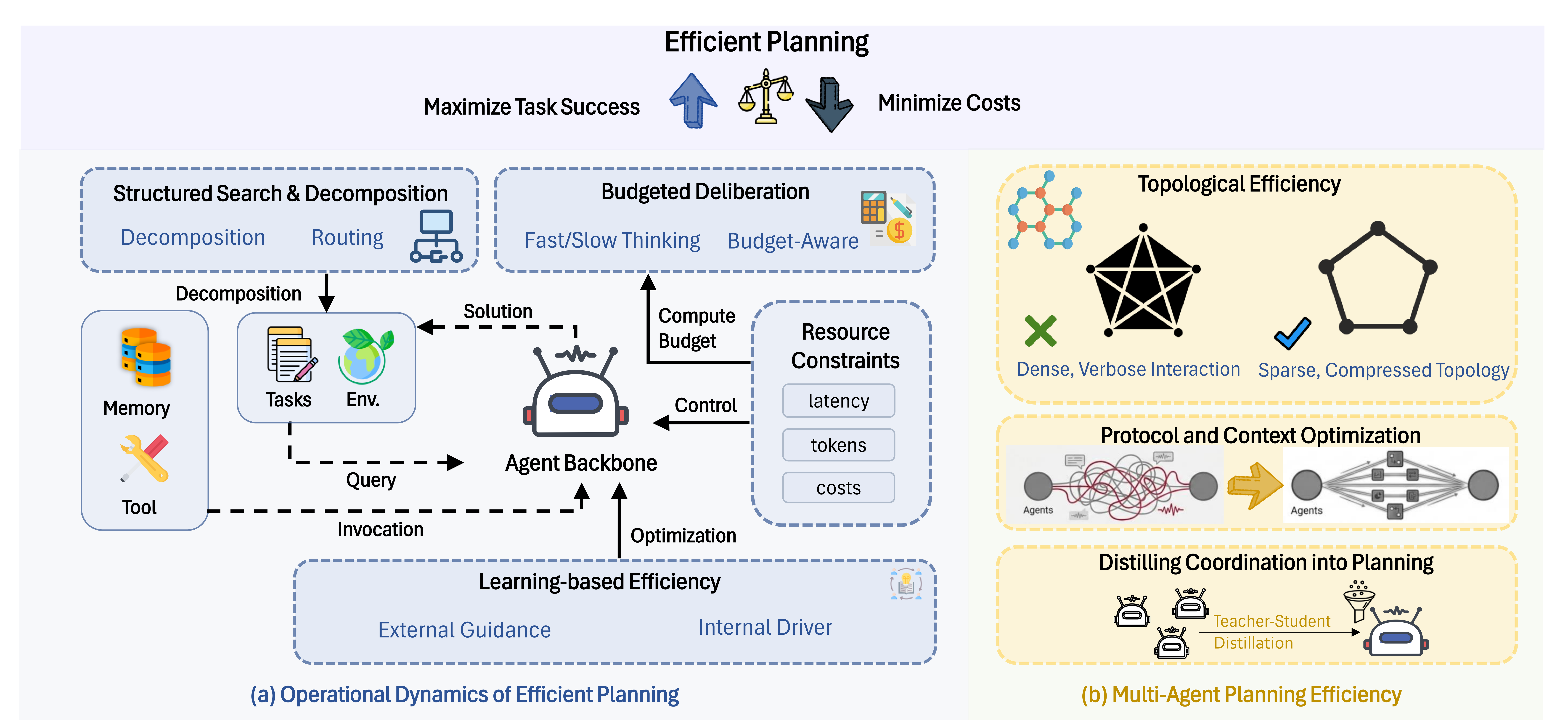
Planning framework encompasses single-agent planning efficiency and multi-agent collaborative strategies for enhanced decision-making.
🤖 Single-Agent Planning Efficiency
💰 Adaptive Budgeting and Control
- (2025-11) Budget-Aware Tool-Use Enables Effective Agent Scaling
- (2025-09) Learning When to Plan: Efficiently Allocating Test-Time Compute for LLM Agents
- (2025-06) Query-Level Uncertainty in Large Language Models
- (2023-12) ReST meets ReAct: Self-Improvement for Multi-Step Reasoning LLM Agent ICLR 2024 Workshop
- (2023-05) SwiftSage: A Generative Agent with Fast and Slow Thinking for Complex Interactive Tasks NeurIPS 2023 spotlight
- (2023-03) Reflexion: Language Agents with Verbal Reinforcement Learning NeurIPS 2023
🔍 Structured Search
- (2025-05) Cost-Augmented Monte Carlo Tree Search for LLM-Assisted Planning
- (2023-12) ProTIP: Progressive Tool Retrieval Improves Planning
- (2023-10) ToolChain*: Efficient Action Space Navigation in Large Language Models with A* Search ICLR 2024 poster
- (2023-10) Language Agent Tree Search Unifies Reasoning Acting and Planning in Language Models ICML 2024
📋 Task Decomposition
- (2025-12) Video-Browser: Towards Agentic Open-web Video Browsing
- (2025-05) Alita: Generalist Agent Enabling Scalable Agentic Reasoning with Minimal Predefinition and Maximal Self-Evolution
- (2025-03) ReSo: A Reward-driven Self-organizing LLM-based Multi-Agent System for Reasoning Tasks EMNLP 2025
- (2024-11) BudgetMLAgent: A Cost-Effective LLM Multi-Agent system for Automating Machine Learning Tasks AIMLSystems 2024
- (2024-02) AutoGPT+P: Affordance-based Task Planning with Large Language Models
- (2023-05) ReWOO: Decoupling Reasoning from Observations for Efficient Augmented Language Models
- (2023-03) HuggingGPT: Solving AI Tasks with ChatGPT and its Friends in Hugging Face NeurIPS 2023
🎯 Policy Optimization
- (2025-09) Planner-R1: Reward Shaping Enables Efficient Agentic RL with Smaller LLMs
- (2025-08) Encouraging Good Processes Without the Need for Good Answers: Reinforcement Learning for LLM Agent Planning EMNLP 2025 Industry
- (2025-05) Planning without Search: Refining Frontier LLMs with Offline Goal-Conditioned RL NeurIPS 2025
- (2025-02) QLASS: Boosting Language Agent Inference via Q-Guided Stepwise Search ICML 2025
- (2024-03) Trial and Error: Exploration-Based Trajectory Optimization for LLM Agents ACL 2024
🧠 Memory and Skill Acquisition
- (2025-10) GAP: Graph-Based Agent Planning with Parallel Tool Use and Reinforcement Learning
- (2024-07) Sibyl: Simple yet Effective Agent Framework for Complex Real-world Reasoning
- (2024-06) GraphReader: Building Graph-based Agent to Enhance Long-Context Abilities of Large Language Models EMNLP 2024 Findings
- (2024-02) Graph-enhanced Large Language Models in Asynchronous Plan Reasoning ICML 2024
- (2023-05) Voyager: An Open-Ended Embodied Agent with Large Language Models TMLR 2024
👥 Multi-Agent Collaborative Efficiency
🕸️ Topological Efficiency and Sparsification
- (2025-09) MARS: toward more efficient multi-agent collaboration for LLM reasoning
- (2025-08) SafeSieve: From Heuristics to Experience in Progressive Pruning for LLM-based Multi-Agent Communication AAAI 2026
- (2025-03) AgentDropout: Dynamic Agent Elimination for Token-Efficient and High-Performance LLM-Based Multi-Agent Collaboration ACL 2025
- (2025-02) S$^2$-MAD: Breaking the Token Barrier to Enhance Multi-Agent Debate Efficiency NAACL 2025
- (2024-10) Cut the Crap: An Economical Communication Pipeline for LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems ICLR 2025
- (2024-09) GroupDebate: Enhancing the Efficiency of Multi-Agent Debate Using Group Discussion
- (2024-06) Scaling Large Language Model-based Multi-Agent Collaboration ICLR 2025
- (2024-06) Chain of Agents: Large Language Models Collaborating on Long-Context Tasks NeurIPS 2024
⚙️ Protocol and Context Optimization
- (2025-10) Stop Wasting Your Tokens: Towards Efficient Runtime Multi-Agent Systems
- (2025-09) Free-MAD: Consensus-Free Multi-Agent Debate
- (2025-07) CONSENSAGENT: Towards Efficient and Effective Consensus in Multi-Agent LLM Interactions Through Sycophancy Mitigation ACL 2025 Findings
- (2025-07) CodeAgents: A Token-Efficient Framework for Codified Multi-Agent Reasoning in LLMs
- (2024-05) Smurfs: Multi-Agent System using Context-Efficient DFSDT for Tool Planning NAACL 2025
📊 Distilling Coordination into Planning
- (2025-11) SMAGDi: Socratic Multi Agent Interaction Graph Distillation for Efficient High Accuracy Reasoning NeurIPS 2025 Workshop
- (2025-06) Debate, Reflect, and Distill: Multi-Agent Feedback with Tree-Structured Preference Optimization for Efficient Language Model Enhancement ACL 2025 Findings
- (2024-02) MAGDi: Structured Distillation of Multi-Agent Interaction Graphs Improves Reasoning in Smaller Language Models ICML 2024
BibTeX
@misc{yang2026efficientagentsmemorytool,
title={Toward Efficient Agents: Memory, Tool learning, and Planning},
author={Xiaofang Yang and Lijun Li and Heng Zhou and Tong Zhu and Xiaoye Qu and Yuchen Fan and Qianshan Wei and Rui Ye and Li Kang and Yiran Qin and Zhiqiang Kou and Daizong Liu and Qi Li and Ning Ding and Siheng Chen and Jing Shao},
year={2026},
eprint={2601.14192},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14192},
}
































































































